Hydrocolloids are a group of natural, water-soluble polymers with colloidal properties. Most hydrocolloids are also fibers. They play crucial roles in the food industry, acting as power players behind the scenes of numerous formulations. Typically derived from plants and seaweed, they act as long-term energy storage or structural building blocks.
Plants and algae produce such natural biopolymers through photosynthesis, adding simple sugars like beads on a string to create larger molecules. They are also produced by fermentation. The process combines simple sugar monomers such as glucose, galactose, or mannose as building blocks and makes it possible to create various molecular weights, primary structures, conformations, and shapes.
There are a lot of similarities in the way nature organizes hydrocolloids, regardless of the source, whether fermentation-derived or from seaweed. For example, cellulose is made up of cellobiose disaccharide building blocks. The same building blocks exist in xanthan except that it adds three monomer sidechains.
Konjac is a tuber made up of glucose and mannose, a glucomannan. Interestingly alginate from red seaweed is also made up of glucose and mannose. Except for the glucose and mannose molecules in alginate are carboxylated. This creates glucuronic acid and mannuronic acid building blocks.
Hydrocolloids are ancient ingredients. Safe, effective, and even healthful, hydrocolloids have been part of the human diet for thousands of years. They are approved for use in food by regulatory agencies such as the FDA and EFSA, and so labeled as “generally considered safe for consumption.” They’re essential in today’s food production due to their ability to improve texture, stability, and shelf-life. Today, hydrocolloids are used throughout the food industry in products such as sauces, dressings, baked goods, dairy products, and beverages.
The science behind hydrocolloids
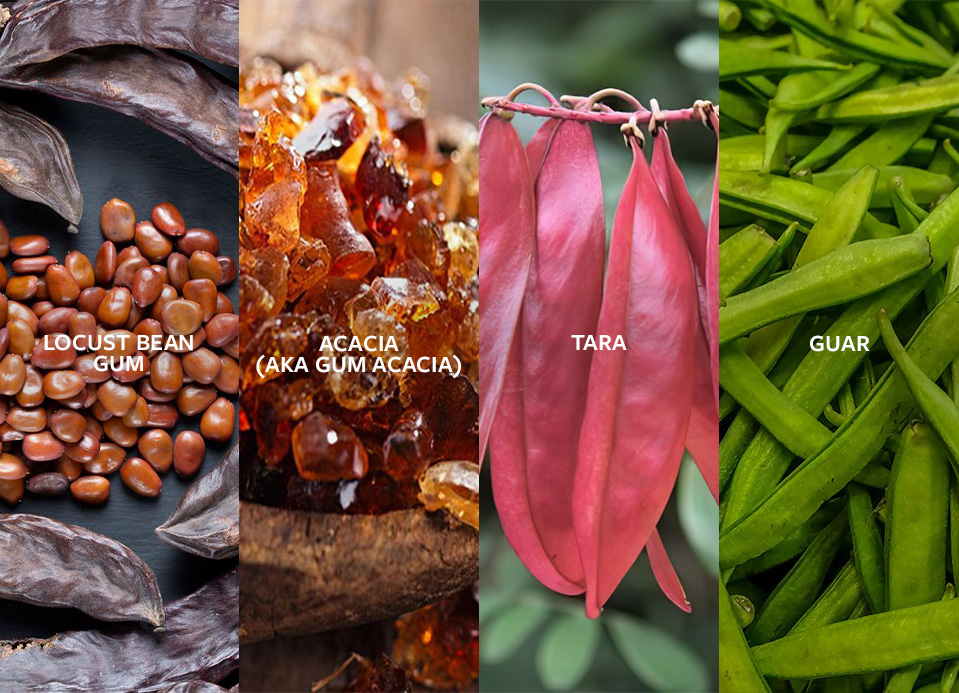
For food scientists, hydrocolloids are long-chain polymers that have the ability to form gels or viscous solutions when dissolved in water. In formulations, they appear as thickening agents, gelling agents, or stabilizers, depending on their properties and applications. Some examples of hydrocolloids commonly used in food products include locust bean gum, tara, guar, acacia, xanthan, agar, carrageenans, and sodium alginate.
In food products, hydrocolloids are clutch players, playing a crucial role in creating a range of textures, providing stability and extending shelf life, and enhancing a food or beverage’s sensory properties. Thickening agents, such as locust bean gum, guar, and tara, are used to increase the viscosity of liquid products while gelling agents like carrageenan and agar are used to create a gel-like texture in food products.
Locust bean gum is used to prevent ice crystal growth in ice cream. Acacia (also known as gum Arabic) is a natural hydrocolloid derived from the sap of the Acacia tree. It’s highly soluble in water and commonly put to use as a stabilizer and emulsifier.
Acacia is best employed in products such as soft drinks, confectionery, and baked goods. It is also used in the production of edible films—thin sheets of hydrocolloids used to wrap food products temporarily.
Just gellin’
Hydrocolloid gels are created by combining a hydrocolloid with water and other ingredients, such as sugar, acid, and salt. The resulting ingredient can be applied to a variety of food applications, especially jams, jellies, and desserts. Hydrocolloid gels also are used in meat products as a binding agent and in dairy products as a thickener.