The main role of hydrocolloids in foods and beverages is to improve the product’s texture, stability, and overall quality. But hydrocolloids do more than help build textures and add to the organoleptic qualities of a product. They also have impressive benefits for health and wellness.
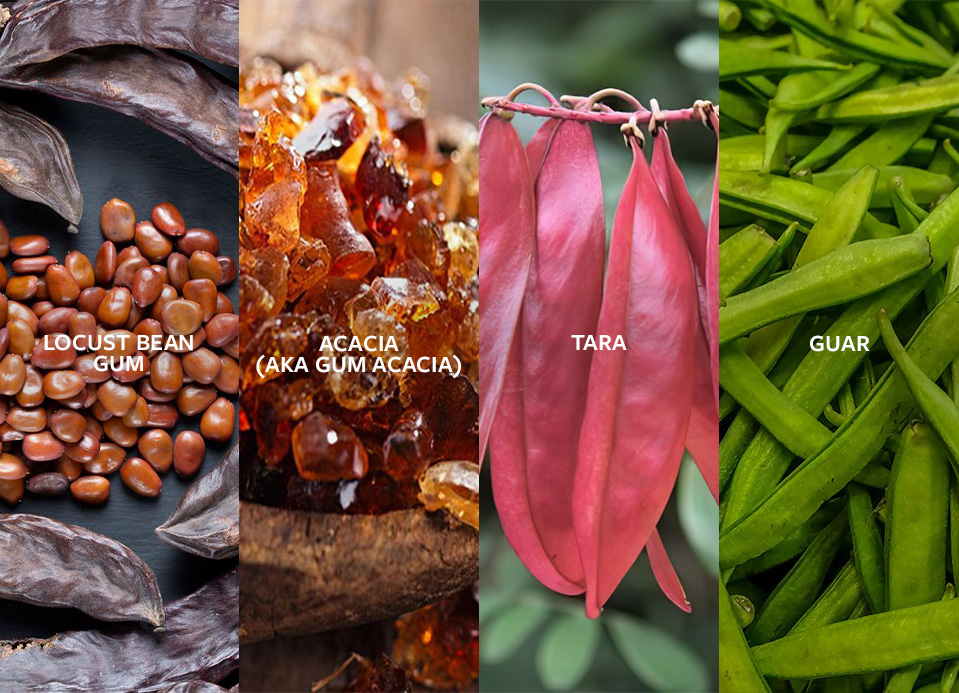
Hydrocolloids are substances, typically polysaccharides or proteins, that can form gels or thicken water when added to an aqueous liquid. They can also bind two immiscible ingredients into a homogenous mixture. In food science, hydrocolloids are biopolymers that are fully soluble in water. Hydrocolloids can be derived from multiple sources, including plants, seaweeds, and microorganisms. While typically used in small amounts, hydrocolloids can have a significant impact on the final product.
Polysaccharidal hydrocolloids are made up of the simple building blocks—monosaccharides—that plants produce as a result of photosynthesis. These building blocks are converted into larger molecules, and polymers, and used as long-term energy storage or structural building blocks.
Hydrocolloids are generally considered safe to use in food. They are classified as food additives and are regulated by food safety organizations such as the FDA in the US, and the EFSA in the EU. The safety of hydrocolloids has been extensively studied, and there is no evidence they are harmful to human health when used in accordance with the recommended levels.
Healthy Three Ways
One main health benefit of polysaccharide hydrocolloids is increasing fiber content. They also can be used to reduce the amount of fat in food products. Hydrocolloids also can be used as a substitute for other ingredients, such as eggs or dairy in vegan or allergy-friendly foods.
As a good source of dietary fiber, they help maintain a healthy digestive system and support immune function. Gut health hydrocolloids also “feed” beneficial gut bacteria, which can improve gut health and reduce the risk of digestive issues and even boost satiety while stimulating the production of short-chain amino acids such as butyrate which help lower the risk of certain cancers. Some hydrocolloids, such as guar and acacia, are particularly high in fiber.
When hydrocolloids are used to replace fat content, they reduce the calorie content of food products, and since some of them are used as a bulking agent, they can even replace part of the sugar content. In this manner, these hydrocolloids can be beneficial for weight management and thus help to reduce the risk of obesity and related health issues.
Blood sugar control studies amply demonstrate that hydrocolloids such as resistant starch or inulin can help to slow the absorption of simple carbohydrates, which can help to regulate blood sugar levels. This can be particularly beneficial for people with diabetes or those at risk of developing diabetes.
Hydrocolloids such as beta-glucans and psyllium have been shown to help reduce cholesterol levels. This can be beneficial for heart health and can help to reduce the risk of heart disease.